1. D. Write a clinical description
This is definitely the most important step - and the place i generally spend the most amount of time. This is the “target” we are trying to phenotype - and if we don’t all have a shared understanding of what we are trying to phenotype - we can not “evaluate” if we are truly identifying the people we want to study in our cohort definitions.
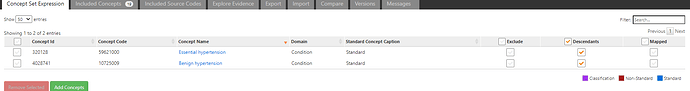
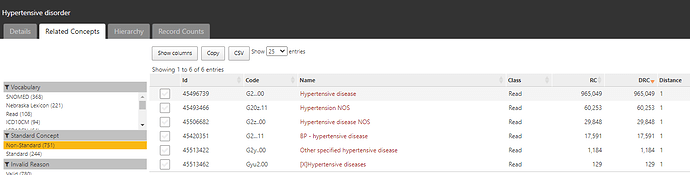
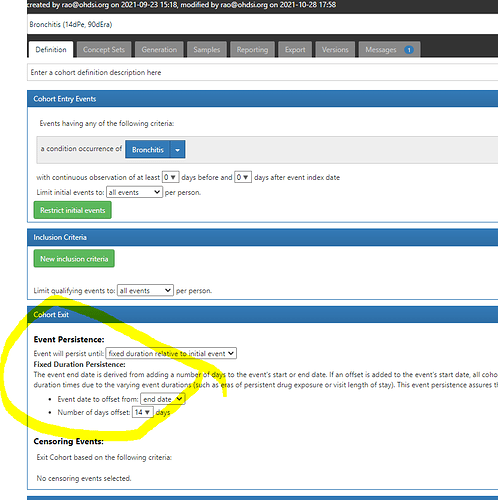
I describe this to be a clinician’s description of a group of persons (patients) current externally observable clinical state. It is expected to be a verbose semi-structured description specified in natural human language, and this is not a computer algorithm or diagnosis code. In fact, at this stage - the phenotyper should NOT be even thinking of implementing the description as either a concept set or cohort definition. If a phenotyper is thinking of codesets NOW - stop - reset - restart. You dont know what you are phenotyping - so dont think of codesets!
My way of introducing structure to this step is by following the same structure that has been used for years in medical training - requiring the following components - Overview, Presentation, Assessment, Plan and Prognosis. Each component is expected to contain at-least one or two lines of clinical knowledge that was synthesized by clinicians (preferably by a panel) with medical knowledge, harvested from authoritative sources like medical text books.
Here are some examples I wrote for phenotyping purposes:
Vitiligo:
Overview: Vitiligo is the most frequent cause of acquired depigmentation disorder of skin that is characterized by development of well-defined white macules on the skin.
Presentation: Vitiligo typically presents with asymptomatic patches of skin that is milky/chalky white in color without signs of inflammation. Although it can appear at any age or anywhere on the body, it has predilection for the face, around orifices, in genitals, and hands. Depigmentation of hair may also occur. Most commonly Vitiligo is non-segmental but can be segmental too especially around the trigeminal nerve distribution.
Assessment: Clinical diagnosis is straightforward based on history and clinical examination. Routine skin biopsy is not needed.
Plan: If rapid progression is suspected, low-dose oral corticosteroids. Phototherapy may cause stabilization.
Prognosis: Clinical course is variable, may remain stable or slowly progress – with extent and distribution changing over lifetime.
Chronic lymphoid leukemia:
Overview: Mature B cell neoplasm characterized by a progressive accumulation of monoclonal B lymphocytes. Similar to non-Hodgkins lymphoma SLL, but the key difference is that this disease manifests primarily in blood, while SLL in primarily lymph node.
Presentation: Most commonly asymptomatic and detected on routine blood test with abnormal lymphocytosis. Occasionally there may be constitutional symptoms like unexplained weight loss, fevers, night sweats, fatigue. CLL does not have lymphadenopathy while non-HL/SLL does.
Assessment: Suspected when there is absolute lymphocytosis on peripheral smear. peripheral blood/bone marrow cell counts, immunophenotypic analysis (flow cytometry), bone marrow biopsy/aspirate, lymph node biopsy/aspirate, spleen.
Plan: Depends on activity of disease/stage; the disease is extremely heterogenous. Nodal disease may involve radiation therapy. There is no single agreed first line therapy.
Prognosis: Chronic disease but may be asymptomatic with minimal progression, or may progress quickly
Lichen planus
Overview: is a rare disease affecting middle aged adults most commonly affecting skin as pruritic, purple, polygonal and papular lesions lasting a few millimeters each, that may coalesce to forms large lesions over time. Common areas of extremities, scalp and genitalia. It may also involve the mucus members of the oral cavity and esophagus. It is commonly associated with hepatitis C.
Presentation: development of pruritic, purple, polygonal, papular lesions in the extremities that are few millimeters in size.
Assessment: clinical examination, no specific testing
Plan: no recommended treatment. Options include corticosteroids, phototherapy.
Prognosis: commonly remits over few years
We cannot phenotype decision:
For me the main indication is - if clinicians are unable to clearly write the clinical idea in this structure - then more than likely this is something we cannot phenotype. Also - if a (panel of) clinician are unable to agree on the clinical description - then we cannot phenotype.












 STOP - RESET - RESTART
STOP - RESET - RESTART