Building on previous work in Phenotype Phebruary 2022
Clinical Description
Defects in neutrophil function can be quantitative, as seen in neutropenia or qualitative, as seen in neutrophil dysfunction. This phenotype is quantitative decrease in neutrophils in persons who previously had normal neutrophil count. Neutropenia is ANC <1500 cells/microL in an adult while agranulocytosis is a more severe form of neutropenia with ANC <200 cells/microL. Note: pancytopenia may include Neutropenia. In this definition, any person with a quantitatively low neutrophil count for any cause is considered to have Neutropenia. Neutropenia may occur due to cytotoxic or marrow toxic drugs (chemotherapy), or in setting of certain diseases like Antineutrophil or autoimmune neutropenia has been observed in autoimmune diseases like Rheumatoid arthritis (Felty syndrome), Inflammatory bowel disease, Sjogren syndrome, Chronic autoimmune hepatitis, Granulomatosis with polyangiitis, or infections like hepatitis, HIV, EBV, HPV, Nutritional deficiency like Hodgkin lymphoma. Presentation: The neutropenia is often asymptomatic or presents with an insidious onset. history of recurrent infections, infections by rare bacteria and fungi, opportunistic infections with observation of low to absent absolute neutrophil count. The clinical presentation is usually oral ulcerations with or without fever, but occasionally sepsis may be the initial presentation. Fever, mouth sores, or gingival disease inflammation. Plan: Find and treat/prevent exposure to offending agent. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) may be used is some scenarios. Prognosis: Neutropenia longer than 2 months is considered chronic neutropenia and since most chemotherapy induced neutropenia is expected to last about 3 weeks, we expect the median to be about 21 days in duration.
Disqualifiers: Normal neutrophil count or elevated neutrophil count that is concurrent is considered not biologically plausible and may indicate bad data. Also persons wtih Familial/congenital neutropenia, benign ethnic neutropenia all time - cannot develop acquired neutropenia (as they may never have had normal neutrophils). Persons post bone marrow transplant are also considered not eligible for aqcuired neutropenia.
Designated Medical Event - MedDRA PT terms:
Granulocytopenia, Has neutropenia as a component: Aplastic anemia, Bone marrow failure, Pancytopenia; Neutropenic colitis, Neutropenic infection, Neutropenic sepsis
Phenotype development:
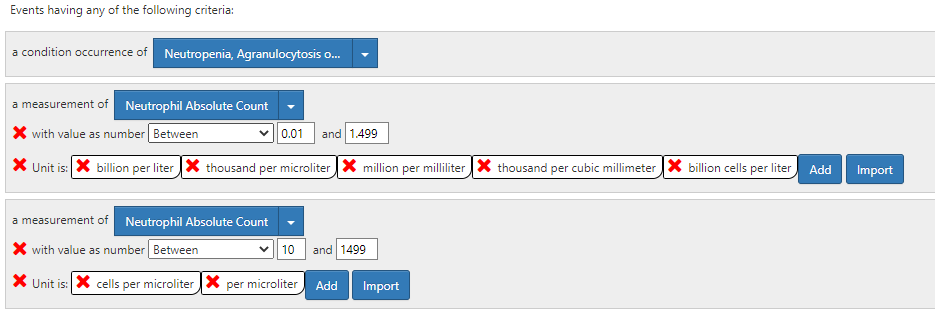
Concept set expression creation: Terms Neutropenia vs Leukopenia: [Decision] Since Neutrophils are the major component of white blood cells (~75%) and the occurrence of having normal neutrophil counts in the presence of low white blood cell count is rare (i.e. we can expect neutropenia in all persons with leukopenia/granulocytopenia) – we decided to consider granulocytopenia and leukopenia as synonyms. However, we decided to not consider the terms lymphocytopenia, eosinopenia as synonyms for neutropenia – as they clearly represent granulocytes that are not neutrophils. An
Use of laboratory results in cohort definitions: [Decision] We decided to use the American Board Of Internal Medicine 2022 laboratory test reference range in the definition, which are as follows: Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) – 2000–8250/μL, 2000 to 8250/microL, 2 to 8.25 x 10/L (SI); Leukocyte count 4000 to 11,000/microL, 4.5 to 11 x 109/L (SI); Segmented neutrophils: 50 to 70 percent. Agranulocytosis < 200.
Congenital or Hereditary Neutropenia vs Acquired Neutropenia: [Decision] Persons with neutropenia may have neutropenia because of congenital or genetic conditions. Those persons cannot have acquired neutropenia. We decided to define Acquired Neutropenia as those persons who do not have a diagnosis of congenital or acquired neutropenia.
Out of scope: Single cell line vs Multiple cell lines: [Decision] Neutropenia may be part of multiple cell line penia’s like pancytopenia’s related to peripheral destruction or (more commonly) bone marrow failure/aplastic anemia. We discussed that persons with neutropenia limited to one cell line vs multiple cell lines were two different sub-types of neutropenia. However, phenotyping these subsets are out of scope of this submission.
Out of scope: Degree of neutropenia: [Decision] Because degree of severity of neutropenia correlates with their risk of infection, phenotyping neutropenia sub-types by degree of severity is important. Severe reduction of neutrophils is agranulocytosis. sub-types by degree of neutropenia is out of scope of this submission.
Data quality: [Decision] We observed that in rare occasions for a person to have a lab result corresponding to neutropenia, while another lab result on the same day is in the normal range. We decided that these may represent FALSE positives, potentially due to lab errors – and decided to remove those individuals.
Cohort Exit [Decision] We assumed that most neutropenia will resolve by around 3 weeks, hence we used a cohort exit persistence criteria of 21 days. We also assumed persons with another episode of neutropenia within 365 days were part of the original neutropenia (e.g. repeat chemotherapy).
Submission:
We submit the cohort definition # 213 to the OHDSI phenotype library which is currently in peer review status. C213: [P] Acquired Neutropenia or unspecified leukopenia (21Pe, 365Era)
Logic Description: all events of neutropenia indexed on diagnosis or lab results with no congenital or genetic neutropenia. Events with concomitant neutrophilia or normal neutrophil counts would be considered bad data and removed.
Phenotype evaluation:
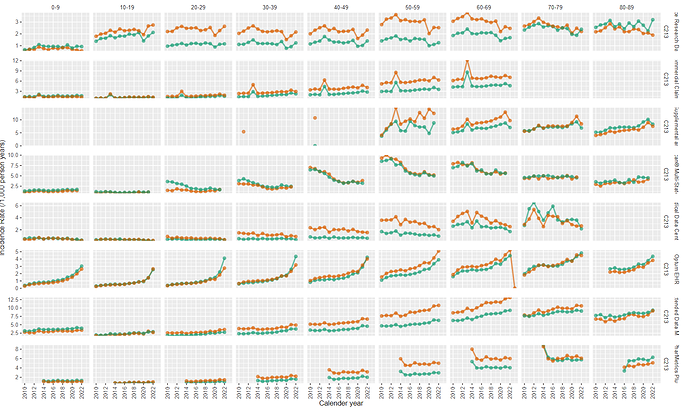
- I observed that we have about 1.1 to 1.2 events per persons with 75%ile of person entries having time in cohort of 21 days. Since 21 days of neutropenia is biologically plausible, I think the cohort exit strategy that utilized 21 days is collapsing any follow-up visits when present.
- Older ages had higher incidence rate compared to younger age, with females > males.
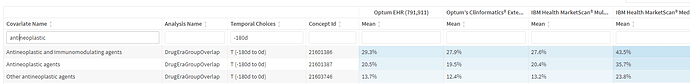
- on review of characterization data, i observed that about 40% of persons may have received chemotherapy.
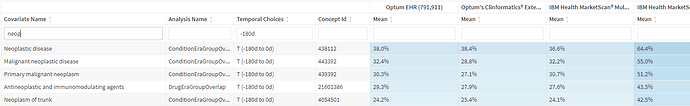
and a vast majority of persons had neoplastic disease
this suggests that the majority of the persons with neutropenia are probably neoplasm or antineoplastic treatment related neutropenia.
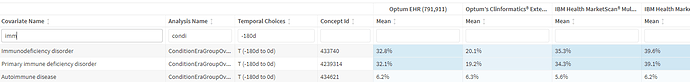
Also prevalent in this population were autoimmune and immunodeficiency conditions (note: congenital neutropenia are removed by design, implying these are all acquired immunodeficiency)
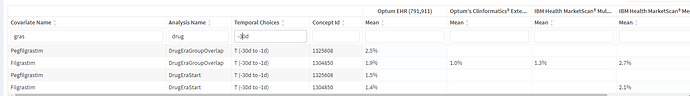
We also observe the use of filgrastim/pegfilgrastim in such persons
Finally we observe some index date misclassificaiton
Other finding in some data sources, the code of neutropenia was not used. It appeared the term of agranulocytosis was used to represent the idea of neutropenia. Reason for this is unclear.